Water-Cooled Helical Rotary Chiller Series R: Annual Maintenance and Checks
This procedure is the recommended annual maintenance of your equipment. This focuses on compressor maintenance, compressor oil, oil level and appearance. You need to have a qualified technician check the settings and function of each control and inspect the condition of and replace compressor and control contacts if needed.
Water-Cooled Helical Rotary Chiller Series R: Annual Maintenance and Checks
This procedure is the recommended annual maintenance of your equipment. This focuses on compressor maintenance, compressor oil, oil level and appearance. You need to have a qualified technician check the settings and function of each control and inspect the condition of and replace compressor and control contacts if needed.
Overview
An important aspect of the chiller maintenance program is the regular completion of operator logs. See “Log and Check Sheets,” p. 157 for an example. When filled out properly the completed logs can be reviewed to identify any developing trends in the chiller's operating conditions
This section describes preventative maintenance procedures and intervals. Use a periodic maintenance program to ensure optimal performance and efficiency of the Series R units.
Maintenance
! WARNING
Hazardous Voltage!
Failure to disconnect power before servicing could result in death or serious injury. Disconnect all electric power, including remote disconnects before servicing. Follow proper lockout/tagout procedures to ensure the power can not be inadvertently energized.
! WARNING
Live Electrical Components!
Failure to follow all electrical safety precautions when exposed to live electrical components could result in death or serious injury. When necessary to work with live electrical components, have a qualified licensed electrician or other individual who has been properly trained in handling live electrical components perform these tasks.
Annual Maintenance and Checks
! WARNING
Hazardous Voltage!
Failure to disconnect power before servicing could result in death or serious injury. Disconnect all electric power, including remote disconnects before servicing. Follow proper lockout/tagout procedures to ensure the power can not be inadvertently energized.
Shut down the chiller once each year to check the following:
Scheduling Other Maintenance
Refrigerant and Oil Charge Management
Proper oil and refrigerant charge is essential for proper unit operation, unit performance, and environmental protection. Only trained and licensed service personnel should service the chiller.
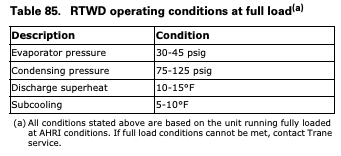
Table 85and Table 86 list baseline measurements for units running at AHRI standard operating conditions. If chiller measurements vary significantly from values listed below, problems may exist with refrigerant and oil charge levels. Contact Trane service.
Note: AHRI conditions are: condenser water: 85°F and 3 GPM per ton and evaporator water: 54-44°F
Heat Exchanger Service
Cleaning the Condenser (RTWD Only)
NOTICE:
Proper Water Treatment!
The use of untreated or improperly treated water could result in scaling, erosion, corrosion, algae or slime. It is recommended that the services of a qualified water treatment specialist be engaged to determine what water treatment, if any, is required. Trane assumes no responsibility for equipment failures which result from untreated or improperly treated water, or saline or brackish water.
Condenser tube fouling is suspect when the “approach” temperature (i.e., the difference between the refrigerant condensing temperature and the leaving condenser water temperature) is higher than predicted.
Standard water applications will operate with less than a 10oF approach. If the approach exceeds 10oF cleaning the condenser tubes is recommended.
Note: Glycol in the water system may as much as double the standard approach.
If the annual condenser tube inspection indicates that the tubes are fouled, two cleaning methods can be used to rid the tubes of contaminants.
! WARNING
Heavy Objects!
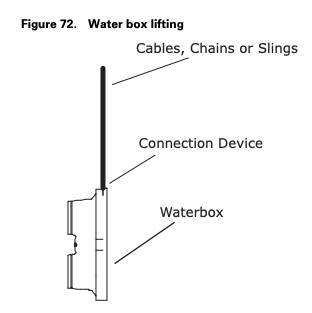
Failure to properly lift waterbox/cover could result in death or serious injury. Each of the individual cables (chains or slings) used to lift the waterbox/cover must be capable of supporting the entire weight of the waterbox/cover. The cables (chains or slings) must be rated for overhead lifting applications with an acceptable working load limit.
! WARNING
Heavy Objects!
Failure to properly lift waterbox could result in death or serious injury. The proper use and ratings for eyebolts can be found in ANSI/ASME standard B18.15. Maximum load rating for eyebolts are based on a straight vertical lift in a gradually increasing manner. Angular lifts will significantly lower maximum loads and should be avoided whenever possible. Loads should always be applied to eyebolts in the plane of the eye, not at some angle to this plane.
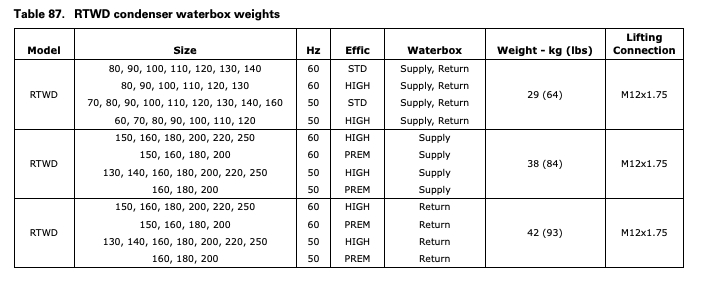
Review mechanical room limitations and determine the safest method or methods of rigging and lifting the waterboxes.
Units with Standard Condenser Waterboxes.
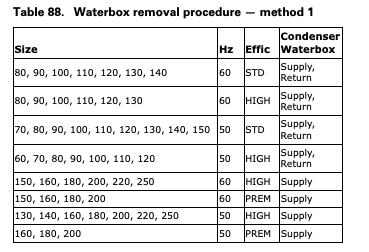
Select the proper waterbox removal procedure method as shown below.
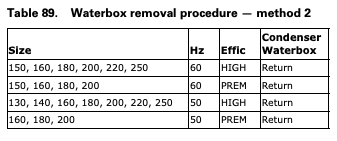
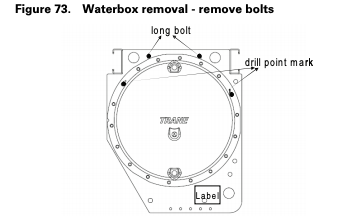
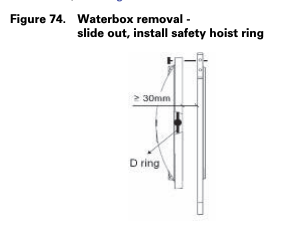
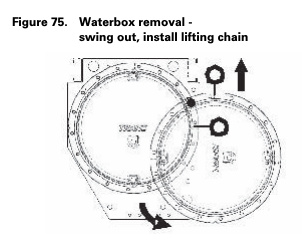
Waterbox Removal Procedure
METHOD 1:
METHOD 2:
! CAUTION
Risk of Injury!
To prevent injury, do not place hands or fingers between waterbox and condenser tubesheet.
! WARNING
Overhead Hazard!
Never stand below or in close proximately to heavy objects while they are suspended from, or being lifted by, a lifting device. Failure to follow these instructions could result in death or serious injuries.
Condenser Tube Cleaning - Mechanical
Reassembly. Once service is complete, the waterbox/ cover should be reinstalled following all previous procedures in reverse.
Chemical Cleaning Procedure
Scale deposits are best removed by chemical means. Consult a qualified water treatment specialist (i.e., one that knows the local water supply chemical/mineral content) for a recommended cleaning solution suitable for the job. (A standard condenser water circuit is composed solely of copper, cast iron and steel.) Improper chemical cleaning can damage tube walls.
All of the materials used in the external circulation system, the quantity of the solution, the duration of the cleaning period, and any required safety precautions should be approved by the company furnishing the materials or performing the cleaning.
Note: Chemical tube cleaning should always be followed by mechanical tube cleaning.
Cleaning the Evaporator
Since the evaporator is typically part of a closed circuit, it does not accumulate appreciable amounts of scale or sludge. However, if cleaning is deemed necessary, use the same cleaning methods described for the condenser tubes.
RTUD Air Cooled Condenser Applications
High Condenser Pressure Limit and High Pressure Cutout Diagnostics
If a circuit experiences significant time in the High Condenser Pressure Limit mode, or if it experiences High Pressure Cutout trip diagnostics, the air cooled condenser may be the root cause and should be inspected.
The condenser coils should be checked for air flow restrictions and cleanliness, as well as the possibility of recirculated air, in which the air entering the coil is significantly higher temperature than the ambient outdoor air temperature (5 ºF or more).
All of the fans should also be validated to be operational with the proper fan blade rotation direction. Dirty, or fouled coils, or otherwise limited or restricted air flow through the coils, can significantly degrade the efficiency of the chiller as well as result in unnecessary limits and nuisance trips. See the condenser manufacturers’ maintenance and cleaning procedures.
Lubrication System
Compressor Oil
NOTICE:
Equipment Damage!
To prevent oil sump heater burnout, open the unit main power disconnect switch before removing oil from the compressor.
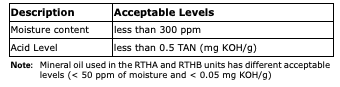
Trane Polyolester Oil is the approved oil for the RTWD/ RTUD units. Polyolester oil is extremely hygroscopic meaning it readily attracts moisture. The oil can not be stored in plastic containers due to the hygroscopic properties. As with mineral oil, if water is in the system it will react with the oil to form acids. Use Table 93 to determine the acceptability of the oil.
Note: Use an oil transfer pump to change the oil regardless of chiller pressure.
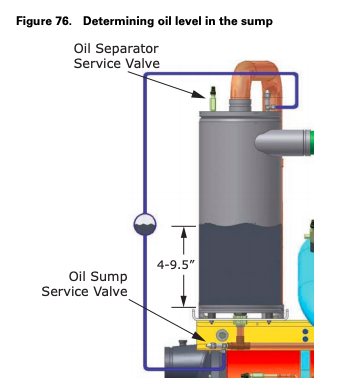
Oil Sump Level Check
Running the chiller at minimum load is the best for the quickest return of oil to the separator and sump. The machine still needs to sit for approximately 30 minutes before the level is taken. At minimum load, the discharge superheat should be highest. The more heat in the oil as it lays in the sump, the more refrigerant will boil off in the sump and leave more concentrated oil.
The oil level in the oil sump can be measured to give an indication of the system oil charge. Follow the procedures below to measure the level.
Source: Trane (www.trane.com)